The SQL Order By allows you to sort your results when you run a SQL Query.
Let-s look at an example:
select * from employee order by employee_name;
This will sort by the **employee_name** column.
Here are the results:

If you want to change the sort from **Ascending** (which is the default) to **Descending**, you would write your query as follows.
select * from employee order by employee_name desc;
With the following results:

You can also sort by more than one column.
select * from employee order by job asc,employee_name desc;
Notice how **job** and **employee_name** columns are both sorted.

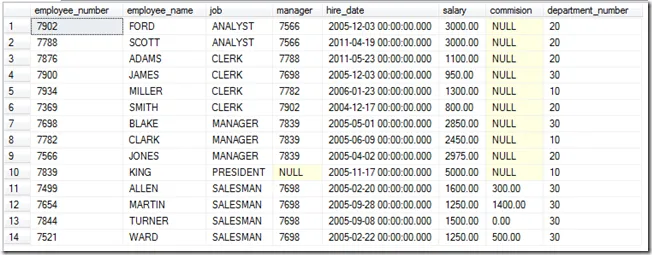
And the last trick is that you can use the column number. In this case I will sort by the 3rd column (job) then the 2nd column (employee_name).
select * from employee order by 3 asc,2 asc;Notice that I changed the employee_name column to sort ascending.
And that-s it for the **SQL Order By **clause.
Leave any comments or questions below.